iehst,Vater,du den Erlkönig nicht?*
Der Erlkönig,written in 1782, is probably
the best-known poem by Johann Wolfgang
von Goethe, and tells how the Erlkönig (=
Alder King) tries to carry off a small boy being
borne on horseback in his father's arms,while
the latter is unaware of the evil presence.
Since time immemorial the Common Alder
(
Alnus glutinosa
) has had a sinister aspect in
folklore. The Alder King may be a figment of
the imagination, but the Alder's habit of
growing in wet, swampy surroundings has
historically given it a less than favorable
reputation among humans. But not among
the pioneers of the aquarium hobby.Anyone
who keeps snakes, toads, and slippery fishes
at home won't be too worried about the
Alder's reputation and will put aside ancient
prejudices against the environment it
inhabits. And thus it was that our forefathers
in the hobby very quickly discovered that the
fruits of the Alder, the so-called Alder cones,
were a first-class natural healing medium.
The Alder from a botanic viewpoint
The genus
Alnus
- alders - is represented by
three species in central Europe. Worldwide
there are between 17 and 50 species,
depending on the opinion of the scientist in
question.The truth probably lies somewhere
in between. All alders are trees or shrubs. But
only the Common Alder is perfectly adapted
towet locations,so there is no risk at all of any
confusion.
NEWS 115
32
It is increasingly being recognizedwithin the framework of close-to-nature fish-
keeping that the maintenance and breeding of fishes, shrimps and other
crustaceans, gastropods, bivalves, and aquatic plants goes better and is more
satisfying themore closely it imitates the example of nature.Anyonewhowants
to take this routewill very soon encounter the largest of all the terrestrial plants,
the trees, along the way. Their branches and roots provide hiding-places, their
leaves form the basis of the food chain in almost all thewaters that are home to
ornamental fishes in thewild,andprovide a lot of small creatureswith their daily
bread. But only a few aquarists are aware of their medicinal properties - pity!
Medicinal trees
Part 1: The Common Alder
by Birgit Bautz-Schäfer
The natural aquarium
S
The Common Alder is a member of the birch
family (Betulaceae), and hence is related to
the birches (
Betula
) and the hazelnuts
(
Corylus
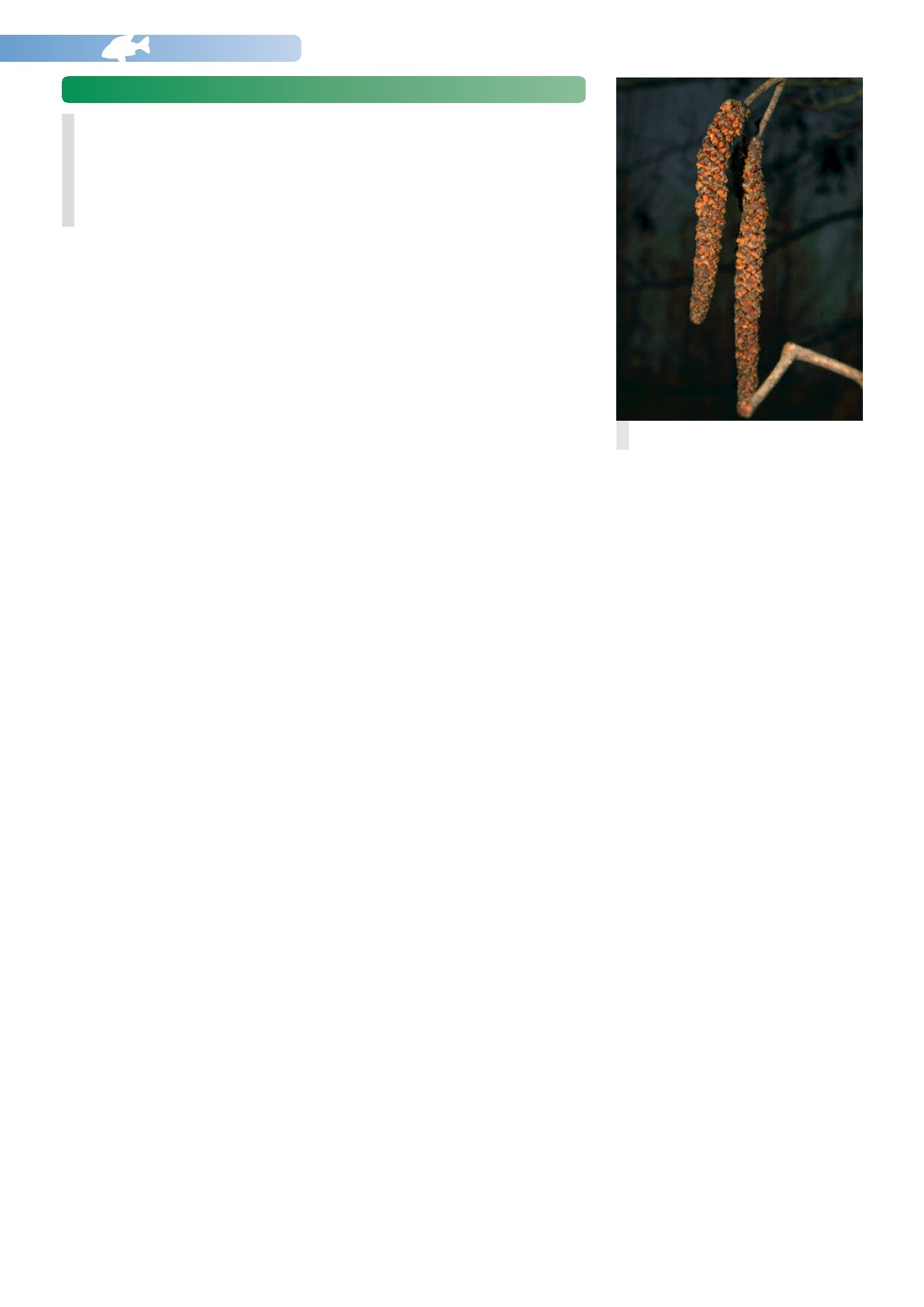
). Like them it has male and female
flowers, both on the same tree. The male
flowers, which produce the pollen, are called
catkins. The female flowers are very
inconspicuous and sit in clumps at the ends
of small twigs. Pollination is effected by the
wind.
Survival specialists
Like all animals and plants on this planet, the
Common Alder requires oxygen for
respiration. Trees that stand in water for any
length of time suffocate and die. But not
Common Alders.Why? The Common Alder is
the only species of European tree with the
ability to take up oxygen from the air via its
trunk and transport it to the roots, where it
can be breathed.In addition,as an adaptation
to nutrient-poor marshy soils, the Alder lives
in symbiosis with bacteria that can bind
nitrogendirect fromthe air.Nitrogen is one of
themost important of all plant nutrients.And
finally,the Common Alder has evolved a host
of decay-limiting substances that prevent the
plant from rotting in the waterlogged
environment in which it lives. It is mainly
these fungicidal and bactericidal substances
that make the Alder so valuable to aquarists.
The effective ingredients
Unfortunately there has been no scientific
research into the precise substances
contained in Alder cones, or at least none is
known to us.But because the bark and leaves
of the Common Alder are used in human
medicine, their contents are well known. As
with all natural products the concentration of
the individual substances varies depending
on the location and the time of collection,but
as a rough rule of thumb it can be stated that
some 10-20% of the contents are tannic
acids, while additional main active
ingredients are phenylpropane (flavonol-
glycoside (hyperoside)), cinnamic acids,
stilbene derivatives, steroids, and triterpenic
acids (taraxerol (alnulin) and taroxeron
(protaenulin)), and ancillary substances are
anthraquinone (emodin), sugars, uric acids,
and waxes (all data after L
AGONI
, 2003).
Usage
In human medicine Alder-bark teas are used
as a gargle to treat inflammation of the
mouth and throat,tooth and throat pain,and
bleeding gums; Alder bark is used to make a
lotion or poultice, and the leaves to treat all
sorts of skin conditions, eczema, infected
wounds, burns, and hemorrhoids. Strange to
say Alder cones aren't used in classic
medicine, though they are used in folk
medicine, to produce an aphrodisiac.
Their use in the aquarium is simplicity itself
and has been tested thousands of times:they
are added to the aquarium at the rate of one
Alder cone per 10-20 liters of water.And that's
it. You can also use a lower dosage - with
natural medications the rule "more helps
more" generally DOESN'T apply. On the
Male Common Alder flower (catkin).
* Father, don
´
t you see the Alder King?


